Please note that this post is tagged as a rumor.
Zen4 CCD has 58% more transistors than Zen3’s
Just hours away from the launch of AMD’s new desktop series, Angstronomics has new information on the new Zen4 chiplets.
According to the site, AMD Ryzen 7000’s CCD manufactured with TSMC N5 node features 6.57 billion transistors, 58% more than Zen3 based on TSMC N7. The CCD codenamed “Durango” is AMD’s next-gen chiplet featuring up to eight Zen4 cores codenamed “Persephone”. New architecture, increased cache and AVX512 instruction support are the main factors for the increased transistors’ density.
AMD Zen4 chiplet has 90 million transistor per square mm, which 40 MTr/mm² more than Zen3. Each of the Zen4 cores has 1MB of L2 cache, twice as big as Zen3’s, while the cache area scaling is smaller. Effectively taking a higher percentage of total die area, but also meaning that logic area has doubled in transistors density, the site reports.
As a consequence, the cooling of the Ryzen 7000 desktop CPU may be more complicated. The 72.5 mm² die with maximum turbo power approaching 170W results in 1.92W per mm², and that’s even without considering the max peak power (PPT) of 230W. For Zen3 CPUs that was 83.74 mm² die with 105W TDP so 1.25 W/mm².
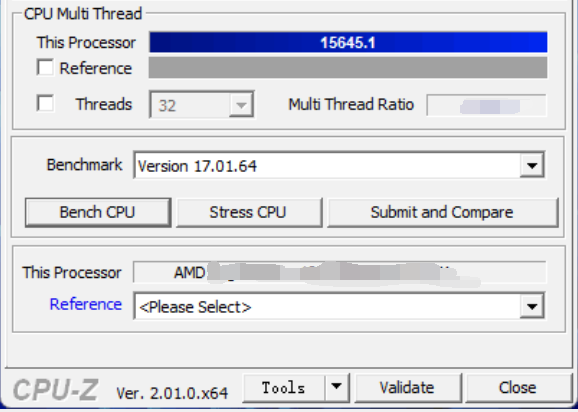
Furthermore, there is also a leak from @OneRaichu featuring 16-core Ryzen 7000 CPUs, so most likely the flagship Ryzen 9 7950X in CPU-Z benchmark. The CPU scores 15645 points in multicore test, which is 8% below leaked Core i9-13900K “Raptor Lake” benchmark results.
Ryzen 9 7950X CPU-Z, Source: @OneRaichu
AMD will officially announce Ryzen 7000 series just 4 hours from now. The new series are expected to launch mid-September with pricing similar to the 5000-series.
Source: Angstronomics, @OneRaichu