By
Illustration to accompany Nature Communications paper, “Seismological expression of the iron spin crossover in ferropericlase in the Earth’s lower mantle.” Credit: Nicoletta Barolini/Columbia Engineering
Multidisciplinary team of materials physicists and geophysicists combine theoretical predictions, simulations, and seismic tomography to find spin transition in the Earth’s mantle.
The interior of the Earth is a mystery, especially at greater depths (> 660 km). Researchers only have seismic tomographic images of this region and, to interpret them, they need to calculate seismic (acoustic) velocities in minerals at high pressures and temperatures. With those calculations, they can create 3D velocity maps and figure out the mineralogy and temperature of the observed regions. When a phase transition occurs in a mineral, such as a crystal structure change under pressure, scientists observe a velocity change, usually a sharp seismic velocity discontinuity.
In 2003, scientists observed in a lab a novel type of phase change in minerals — a spin change in iron in ferropericlase, the second most abundant component of the Earth’s lower mantle. A spin change, or spin crossover, can happen in minerals like ferropericlase under an external stimulus, such as pressure or temperature. Over the next few years, experimental and theoretical groups confirmed this phase change in both ferropericlase and bridgmanite, the most abundant phase of the lower mantle. But no one was quite sure why or where this was happening.
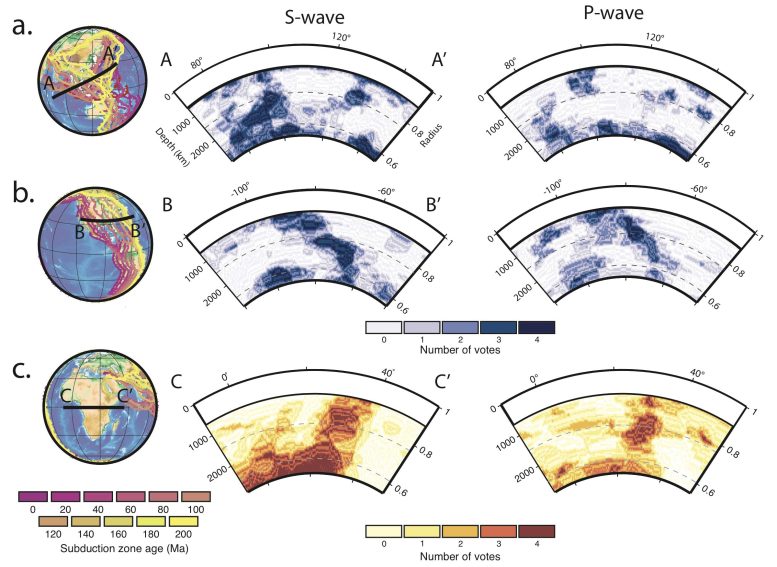
Cold, subducting oceanic plates are seen as fast velocity regions in (a) and (b), and warm rising mantle rock is seen as slow velocity regions in (c). Plates and plumes produce a coherent tomographic signal in S-wave models, but the signal partially disappears in P-wave models. Credit: Columbia Engineering
In 2006, Columbia Engineering Professor Renata Wentzcovitch published her first paper on ferropericlase, providing a theory for the spin crossover in this mineral. Her theory suggested it happened across a thousand kilometers in the lower mantle. Since then, Wentzcovitch, who is a professor in the applied physics and applied mathematics department, earth and environmental sciences, and Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory at (function(d, s, id){
var js, fjs = d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0];
if (d.getElementById(id)) return;
js = d.createElement(s); js.id = id;
js.src = "https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/sdk.js#xfbml=1&version=v2.6";
fjs.parentNode.insertBefore(js, fjs);
}(document, 'script', 'facebook-jssdk'));
Read original article here