A powerful eye in the sky is helping scientists spy “super-emitters” of methane, a greenhouse gas about 80 times more potent than carbon dioxide.
That observer is NASA’s Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation instrument, or EMIT for short. EMIT has been mapping the chemical composition of dust throughout Earth’s desert regions since being installed on the exterior of the International Space Station (ISS) in July, helping researchers understand how airborne dust affects climate.
That’s the main goal of EMIT’s mission. But it’s making another, less expected contribution to climate studies as well, NASA officials announced on Tuesday (Oct. 25). The instrument is identifying huge plumes of heat-trapping methane gas around the world — more than 50 of them already, in fact.
Related: Climate change: Causes and effects
“Reining in methane emissions is key to limiting global warming. This exciting new development will not only help researchers better pinpoint where methane leaks are coming from, but also provide insight on how they can be addressed — quickly,” NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said in a statement (opens in new tab).
“The International Space Station and NASA’s more than two dozen satellites and instruments in space have long been invaluable in determining changes to the Earth’s climate,” Nelson added. “EMIT is proving to be a critical tool in our toolbox to measure this potent greenhouse gas — and stop it at the source.”
EMIT is an imaging spectrometer designed to identify the chemical fingerprints of a variety of minerals on Earth’s surface. The ability to spot methane as well is a sort of happy accident.
“It turns out that methane also has a spectral signature in the same wavelength range, and that’s what has allowed us to be sensitive to methane,” EMIT principal investigator Robert Green, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California, said during a press conference on Tuesday afternoon.
Green and other EMIT team members gave some examples of the instrument’s sensitivity during the Tuesday media call. For example, the instrument detected a plume of methane — also known as natural gas — at least 3 miles (4.8 kilometers) long in the sky above an Iranian landfill. This newfound super-emitter is pumping about 18,700 pounds (8,500 kilograms) of methane into the air every hour, the researchers said.
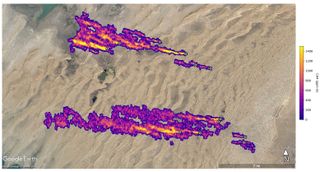
That’s a lot, but it pales in comparison to a cluster of 12 super-emitters EMIT spotted in Turkmenistan, all of them associated with oil and gas infrastructure. Some of those plumes are up to 20 miles (32 km) long, and, together, they’re adding about 111,000 pounds (50,400 kg) of methane to Earth’s atmosphere per hour.
That’s comparable to the peak rates of the Aliso Canyon leak, one of the largest methane releases in U.S. history. (The Aliso Canyon event, which occurred at a Southern California methane storage facility, was first noticed in October 2015 and wasn’t fully plugged until February 2016.)
EMIT spotted all of these super-emitters very early, during the instrument’s checkout phase. So it should make even greater contributions as it gets fully up and running, and as scientists gain more familiarity with the instrument’s capabilities, team members said.
“We are really only scratching the surface of EMIT’s potential for mapping greenhouse gases,” Andrew Thorpe, a research technologist at JPL, said during Tuesday’s press conference. “We’re really excited about EMIT’s potential for reducing emissions from human activity by pinpointing these emission sources.”
Mike Wall is the author of “Out There (opens in new tab)” (Grand Central Publishing, 2018; illustrated by Karl Tate), a book about the search for alien life. Follow him on Twitter @michaeldwall (opens in new tab). Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom (opens in new tab) or on Facebook (opens in new tab).