In this illustration, the multilayered sunshield on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope stretches out beneath the observatory’s honeycomb mirror. The sunshield is the first step in cooling down Webb’s infrared instruments, but the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) requires additional help to reach its operating temperature. Credit: NASA GSFC/CIL/Adriana Manrique Gutierrez
The beam of light coming from the telescope enters MIRI through the pick-off mirror located at the top of the instrument and acting like a periscope. Then, a series of mirrors redirect the light toward the bottom of the instruments where a set of 4 spectroscopic modules are located. Once there, the beam of light is divided by optical elements called dichroics in 4 beams corresponding to different parts of the mid-infrared region. Each beam enters its own integral field unit; these components split and reformat the light from the whole field of view, ready to be dispersed into spectra. This requires the light to be folded, bounced, and split many times, making this probably one of Webb’s most complex light paths. To finish this amazing voyage, the light of each beam is dispersed by gratings, creating spectra that then projects on 2 MIRI detectors (2 beams per detector). An amazing feat of engineering! Credit: ESA/ATG medialab
The low temperature is necessary because all four of Webb’s instruments detect infrared light – wavelengths slightly longer than those that human eyes can see. Distant galaxies, stars hidden in cocoons of dust, and planets outside our solar system all emit infrared light. But so do other warm objects, including Webb’s own electronics and optics hardware. Cooling down the four instruments’ detectors and the surrounding hardware suppresses those infrared emissions. MIRI detects longer infrared wavelengths than the other three instruments, which means it needs to be even colder.
Another reason Webb’s detectors need to be cold is to suppress something called dark current, or electric current created by the vibration of atoms in the detectors themselves. Dark current mimics a true signal in the detectors, giving the false impression that they have been hit by light from an external source. Those false signals can drown out the real signals astronomers want to find. Since temperature is a measurement of how fast the atoms in the detector are vibrating, reducing the temperature means less vibration, which in turn means less dark current.
MIRI’s ability to detect longer infrared wavelengths also makes it more sensitive to dark current, so it needs to be colder than the other instruments to fully remove that effect. For every degree the instrument temperature goes up, the dark current goes up by a factor of about 10.
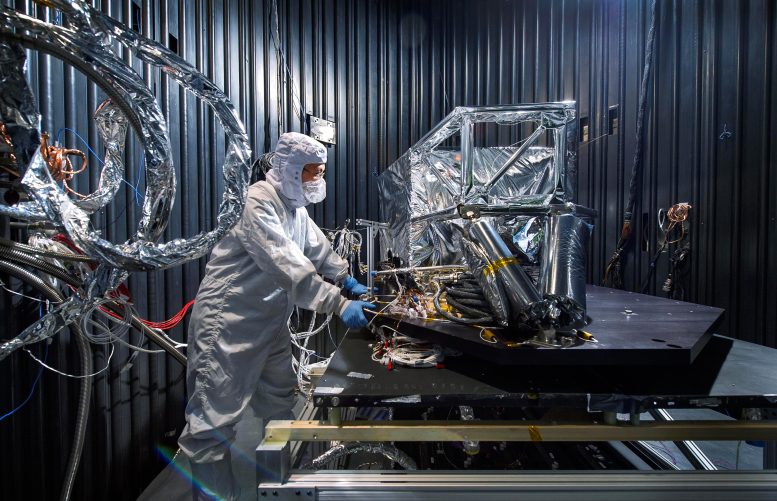
NASA testing the Webb telescope’s MIRI thermal shield in a thermal vacuum chamber at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. Credit: NASA
Once MIRI reached a frigid 6.4 kelvins, scientists began a series of checks to make sure the detectors were operating as expected. Like a doctor searching for any sign of illness, the MIRI team looks at data describing the instrument’s health, then gives the instrument a series of commands to see if it can execute tasks correctly. This milestone is the culmination of work by scientists and engineers at multiple institutions in addition to Read original article here
